
The year 2016 is characterized by a significant increase in electricity consumption at 10% and peak demand at 8.7% attributed to several factors such as the increase in temperature and utilization of cooling equipment aggravated by the strong El Niño, the conduct of National and Local elections during the first half of the year, increase in economic growth, and entry of large power generating plants. The residential and industrial sectors remained the major drivers of electricity consumption in the country while Luzon remained the largest on a per grid basis.
Notably, the growth of the country’s supply base supplemented the increase in demand with the growth of total installed capacity at 14% from 18,765 MWh (2015) to 21,423 MWh (2016) majority coming from coal-fired power plants. Among the three grids, Mindanao has the highest recorded growth in terms of capacity at 31% from 2015-2016. From 2017-2025 a total of 5,068 MW committed projects are expected to come online. The DOE is continuously encouraging investments in power generation in view of the increasing peak demand which is expected to grow by more than triple* in 2040.
Along with supply security, the DOE also embarks on increasing the reliability and resiliency of the system. In 2016, several yellow and red alerts were declared by the system operator in Luzon and Visayas in addition to the major grid disturbances and load dropping incidents. Among the three major grids, Mindanao was adversely affected by El Niño which caused the decline in hydro power generation and curtailment of supply during the first half of 2016. The entry of large coal-fired power plants in Mindanao on the latter part of 2016 has addressed these supply shortfalls.


Electricity Sales and Consumption Highlights
-
Electricity consumption grew significantly from 82,413,213 MWh (2015) to 90,797,891 MWh (2016). This year’s growth level increased to 10.2% compared to the 6.7% growth from 2014-2015. The substantial increase is due to the strong El Niño which affected the entire country during the 1st half of 2016.
-
This increase is primarily driven by the growth of residential consumption at 12.7% from 22,747,049 MWh (2015) to 25,631,254 MWh (2016) due to high requirements for cooling system.
-
On a per grid basis, Mindanao’s electricity consumption grew the highest at 12% boosted by the own-use consumption of newly operational and large coal-fired power plants. Own-use consumption in Mindanao massively increased from 395,268 MWh to 651,156 MWh which is equivalent to a 64.7% growth rate in 2016.
-
In terms of share, Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao contributed 74%, 13.5% and 12.5% shares, respectively. The residential sector, together with the industrial sector, comprised more than half of the total Philippine electricity consumption. Own-use and systems loss have at par shares at 9%.
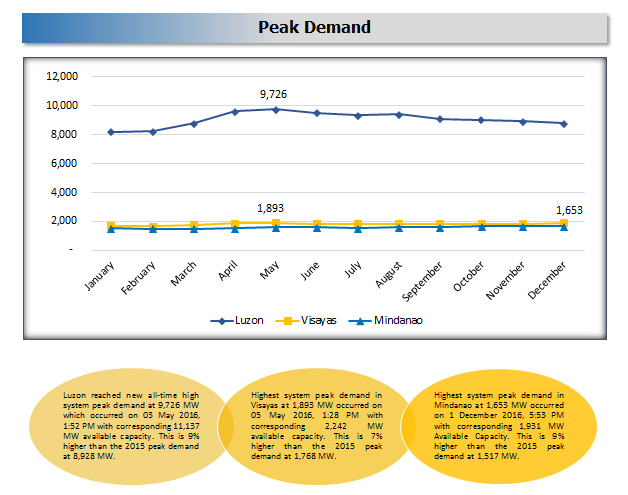
Comparative Peak Demand, Actual 2015-2016 vs. Forecast
|
Grid |
2015 Actual (MW) |
2016 Actual (MW) |
Difference (MW) |
2015-2016 Growth Rate |
PDP 2016 High GDP Forecast (MW) |
Difference of 2016 Forecast vs. Actual (MW) |
2016 Forecast vs. Actual Deviation |
|
Luzon |
8,928 |
9,726 |
798 |
8.94% |
9,726* |
0 |
0 |
|
Visayas |
1,768 |
1,893 |
125 |
7.07% |
1,878 |
(15) |
(0.8)% |
|
Mindanao |
1,517 |
1,653 |
136 |
8.97% |
1,786 |
133 |
8.0% |
* Actual 2016 Peak Demand was already adopted in the PDP, 2016-2040 since the peak demand already occurred prior to the finalization of the PDP, 2016-2040

The country’s total installed capacity for 2016 grew to 21,423 MW compared to 18,765 MW from 2015. This increase in capacity is associated with the commercial operation of new power plants in Luzon such as the 2x150 MW SLPGC Coal Power Plant, 450 MW San Gabriel Natural Gas Power Plant; Visayas the 135 MW Palm Concepcion Coal Power Plant Unit 1, 132.5 MW HELIOS Solar Farm; and Mindanao the 2 x 135 MW FDC Misamis Coal Power Plant, and 150 MW SMC Malita Coal Power Plant. On the other hand, the country has a total of 19,097 MW dependable capacity or about 89% of the total installed capacity which has been delivered to the grid.
The Philippines also displayed a significant growth in power generation at 10% from 82,413,213 MW in 2015 to 90,797,891 MW in 2016. Of this total generation, 48% comes from coal, 22% comes from natural gas and 6% comes from oil-based generation. The remaining 24% or about one-fourth of the total power generation comes from renewable energy (RE) – based generating facilities.

Read more on 2016 Philippine Power Situation
ANNEXES
Annex 1. Luzon Actual 2016 Electricity Demand-Supply Situation
Annex 2. Visayas Actual 2016 Electricity Demand-Supply Situation
Annex 3. Mindanao Actual 2016 Electricity Demand-Supply Situation
Annex 4. 2016 List of Existing Power Plants, Philippines
Annex 5. 2016 List of Existing Power Plants, Luzon
Annex 6. 2016 List of Existing Power Plants, Visayas
Annex 7. 2016 List of Existing Power Plants, Mindanao
Annex 8. Luzon Grid Committed Power Projects As of 31 December 2016
Annex 9. Luzon Grid Indicative Power Projects As of 31 December 2016
Annex 10. Visayas Grid Committed Power Projects As of 31 December 2016
Annex 11. Visayas Grid Indicative Power Projects As of 31 December 2016
Annex 12. Mindanao Grid Committed Power Projects As of 31 December 2016
Annex 13. Mindanao Grid Indicative Power Projects As of 31 December 2016
Annex 14. Electricity Sales and Consumption by Sector, 2003-2016 (in GWh).
Annex 15. Electricity Sales and Consumption by Sector, per Grid, 2003-2016 (in GWh).
Annex 16. Annual System Peak Demand per Grid, 1985-2016 (in MW).
Annex 17. Visayas Annual System Peak Demand per Sub-Grid, 1995-2016 (in MW)
Annex 18. Luzon Monthly System Peak Demand, 2001-2016 (in MW)
Annex 19. Visayas Monthly System Peak Demand, 2001-2016 (in MW)
Annex 20. Mindanao Monthly System Peak Demand, 2001-2016 (in MW)
Annex 21. Philippine Gross Generation by Plant Type, 2003-2016 (in GWh)
Annex 22. Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao Gross Generation by Plant Type, 2003-2016 (in GWh)
Annex 23. Visayas Subgrid Gross Generation by Plant Type, 2003-2016 (in GWh)
Annex 24. Gross Power Generation by Ownership, 2003-2016 (in GWh)
